Building Enterprise AI Agents: Technical Implementation

After several months of architecting enterprise AI agents, I have collected some experience with specific technical details that actually matter for production deployments. First of all, AI agents are useful assistants helping people work more efficiently and solve complex tasks. Normally they aren’t individual agents but part of a hierarchical architecture that includes three layers. Humans interact with assistants (the first layer) in natural language similar to how they work with subordinates. These assistants orchestrate AI agents in the second layer that perform specific functions. And functional AI agents of the second layer use multiple different tools of the third layer to integrate with internal and external data sources and perform specific operations.
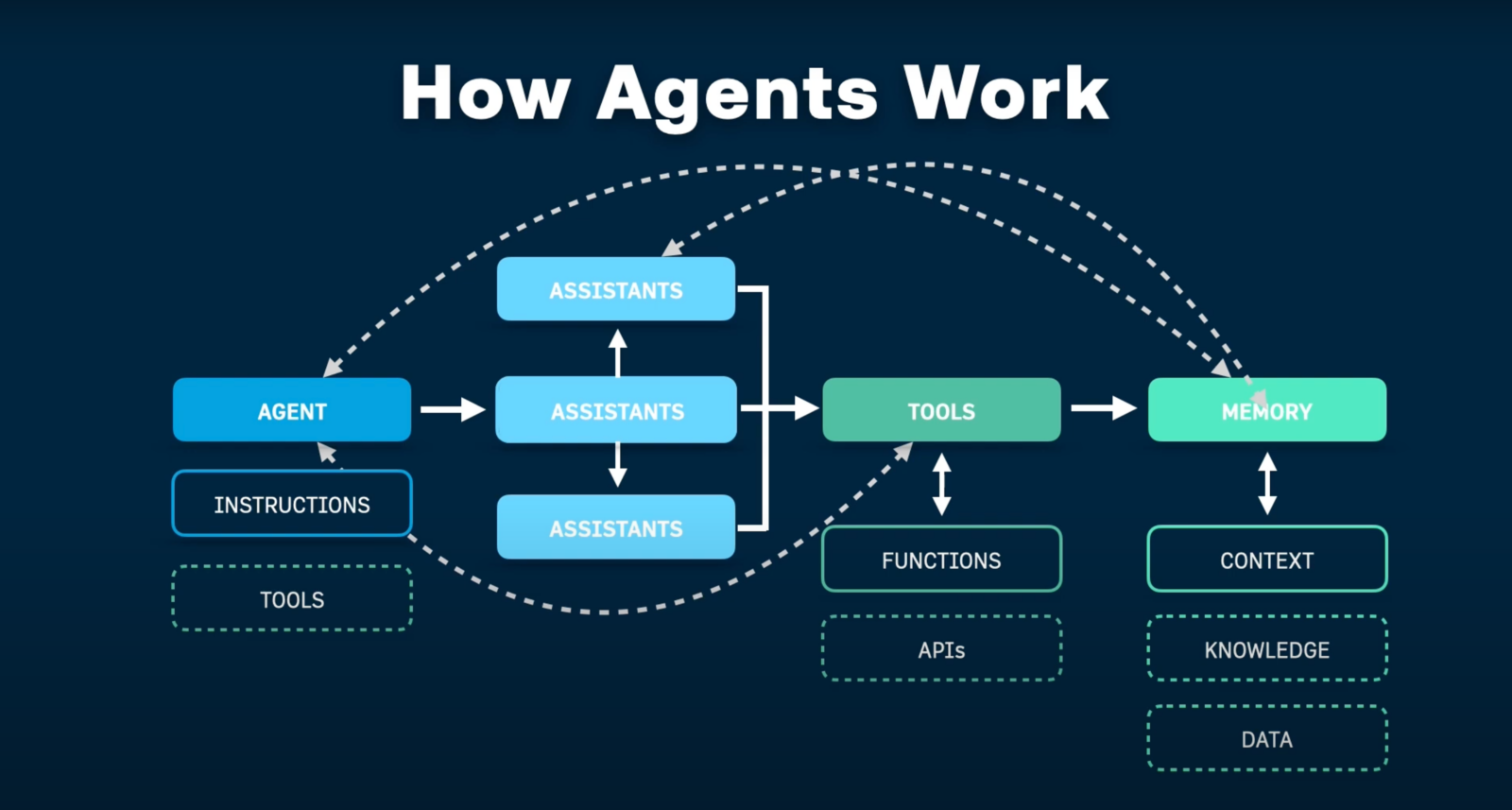
Three-Layer Architecture in Practice
Layer 1: Domain-Specific Agent Assistant
- Customer Service Agent: Multi-channel management across phone/email/chat with intelligent ticket routing based on customer priority and issue complexity. Real integration with Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics for complete lifecycle management.
- Finance Agent: Automated invoice processing, accounts receivable management, budget variance analysis with automated alerting. Direct ERP connectivity (SAP, Oracle, NetSuite).
- Marketing Agent: Campaign execution with dynamic content creation, lead scoring based on behavioral patterns, A/B testing coordination with ROI analysis.
Layer 2: AI Functional Agents
- NLP Agent: Multi-language entity extraction, sentiment analysis with emotion detection, conversation flow management with context maintenance.
- Decision Engine: Rule-based decision making with complex conditional logic, multi-criteria analysis for business scenarios, dynamic threshold adjustment.
- Workflow Orchestration: Process flow management with conditional branching, error handling with rollback capabilities, state management across distributed systems.
Layer 3: Tools Layer
- Database connectors: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Pinecone, Neo4j, Redis with connection pooling.
- Enterprise integrations: Salesforce APIs, Slack/Teams webhooks, document management systems.
- Real-time streaming: Apache Kafka integration for event-driven processing.
Major concerns
Any company dealing with AI agents faces many challenges in AI agents implementation, and this is where the true challenging work begins. Even in my CFO role, I’m not sure whether I can share our proprietary data with AI agents, and how I should assess the forecasts the AI model provides. There are plenty of concerns that should be addressed in AI agent development, and these concerns affect technical implementation and reduce the economic effect of the usage of AI agents.
- Information security, privacy, cross-border operations, and compliance
- Restricted data access limited to users/groups
- Results verification and control, ground truth validation using human-in-the-loop review
- Multiple model selection and orchestration
- Integration complexity
- Infrastructure costs (LLMs) and ROI
Industry benefits
The technical complexity here isn’t the AI models themselves—it’s the enterprise integration, security compliance, and quality assurance systems that make these agents production-ready for regulated industries. From my perspective, Enterprise Corporations (500+ employees) from specific industries benefit more from AI agent implementation:
- Financial Services: Compliance automation, fraud detection with real-time monitoring.
- Healthcare: Patient interaction management, appointment scheduling, HIPAA-compliant data handling.
- E-commerce: Customer support automation, inventory management, personalized recommendation engines.
- Manufacturing: Supply chain optimization, quality control, predictive maintenance.